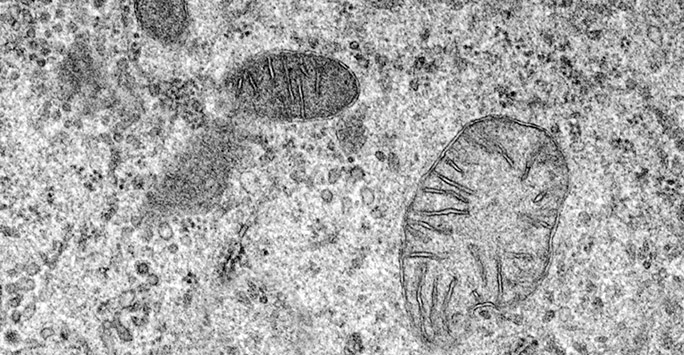
How does the Transmission Electron Microscope work?
Read about how a transmission electron microscope (TEM) captures images of samples.

Sample preparation
Find out about the best way to prepare samples in order to preserve their structure.
Cryo-techniques
Read about how specimens are fixed to preserve them as close to their physiological state as possible.
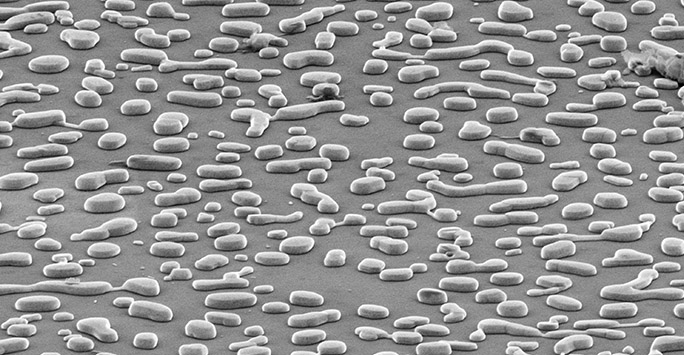
Negative staining
Find out how negative staining helps to preserve structural details of specimens