Single-cell proteomic and transcriptomic analysis of macrophage heterogeneity using SCoPE2
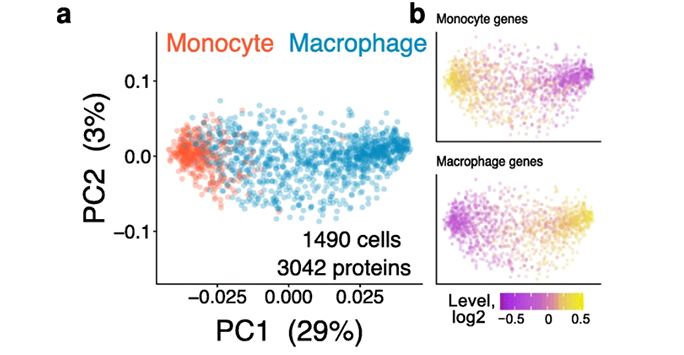
Image: Principal component analysis of proteomic data (a) acquired using SCoPE2 demonstrating clustering of monocyte and macrophage cells. Cells are classified based on the gene level typical of these cells. (b)
Macrophages are innate immune cells with diverse functional and molecular phenotypes. This diversity is largely unexplored at the level of single-cell proteomes because of the limitations of quantitative single-cell protein analysis. To overcome this limitation, we develop SCoPE2, which substantially increases quantitative accuracy and throughput while lowering cost and hands-on time by introducing automated and miniaturised sample preparation.
These advances enable us to analyse the emergence of cellular heterogeneity as homogeneous monocytes differentiate into macrophage-like cells in the absence of polarising cytokines. SCoPE2 quantifies over 3042 proteins in 1490 single monocytes and macrophages in 10 days of instrument time, and the quantified proteins allow us to discern single cells by cell type.
Furthermore, the data uncover a continuous gradient of proteome states for the macrophages, suggesting that macrophage heterogeneity may emerge in the absence of polarizing cytokines. Parallel measurements of transcripts by 10× Genomics suggest that our measurements sample 20-fold more protein copies than RNA copies per gene, and thus, SCoPE2 supports quantification with improved count statistics. This allowed exploring regulatory interactions, such as interactions between the tumor suppressor p53, its transcript, and the transcripts of genes regulated by p53.
Back to: Centre for Proteome Research (CPR)