UHDpulse: A new European research project

UHDpulse - Metrology for advanced radiotherapy using particle beams with ultra-high pulse dose rates is a Joint Research Project with 3-year duration launched in September 2019. It brings together 16 institutes from 8 countries and consists of European metrology institutes, universities, research institutes, and university hospitals in the field of radiation dosimetry and dosimetry detector development.
The project aims to develop and improve dosimetry standards and dose measurement methods for the novel radiotherapy modalities FLASH radiotherapy and very high electron energy (VHEE) radiotherapy as well as for laser-driven medical accelerators. The existing primary standards and dosimetry tools used in conventional radiotherapy are not applicable due to the ultra-high dose rate (UHD) in short beam pulses at these novel radiotherapy techniques. However, accurate measurement of radiation doses is crucial for comparison of preclinical radiobiological studies against each other and for comparison with established treatment modalities. It is vital for delivering successful radiation therapy.
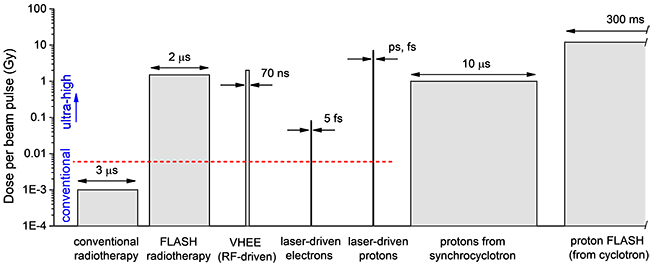
Typical dose per beam pulse and pulse length in conventional and novel radiotherapy techniques.
The project partners will respond the challenge in four work packages (WP). WP1 is focused on primary standards of absorbed dose to water including the establishment of reference radiation fields. WP2 deals with secondary standards and their traceability, relative dosimetry, and characterization on current radiation detectors. In WP3 and WP4 selected current and newly developed radiation detectors are tested, characterized and optimized for measurement of absorbed dose in and outside of UHD primary beams. Recommendations on the basis of the knowledge gained in the project will be summarized in a code of practice.
Interested institutes that want to contribute to the goals of the project may join the consortium as a collaborator. More information about the project can be found on the project home page:
This project has received funding from the EMPIR programme co-financed by the Participating States and from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme.