Underwater volcano behaviour captured by timely scientific expedition
Published on
An international team of researchers got a rare opportunity to study an underwater volcano in the Caribbean when it erupted while they were surveying the area.
The research, published in the journal Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, provides new insight into the little-studied world of underwater volcanoes. It investigated a volcano named Kick-‘em-Jenny (KeJ), which is thought to be named after the turbulent waters nearby.
The team from Liverpool, Imperial College London and Southampton universities, in collaboration with the University of the West Indies Seismic Research Centre (SRC), were collecting ocean-bottom seismometers aboard the NERC research ship R.R.S. James Cook as part of a larger experiment when they were alerted to the volcano erupting.
Direct observation of submarine eruptions are very rare, but having the ship nearby allowed them to get to the volcano in time to record the immediate aftermath of the eruption.
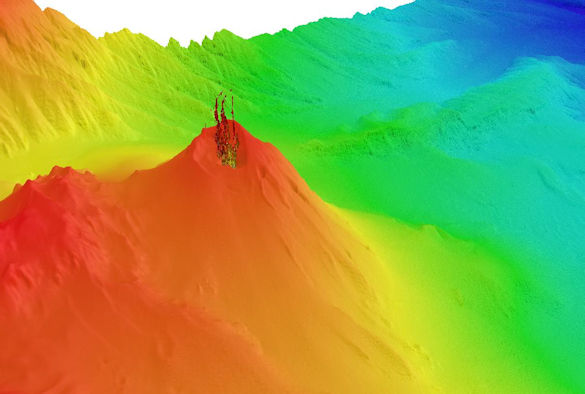
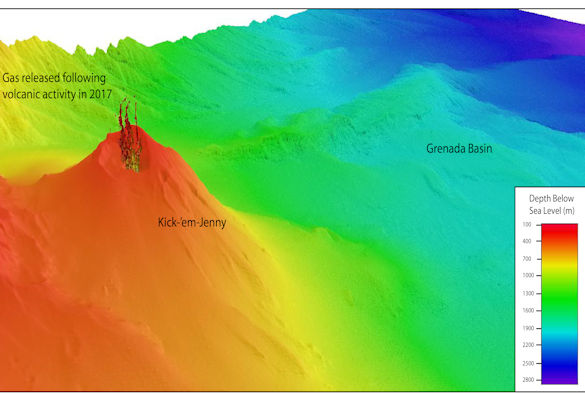
Using ship-based imaging technology, the team was able to survey the volcano, observing gas coming from the central cone. The data was then combined with previous surveys going back more than 30 years to reveal the long-term pattern of activity.
Kick-‘em-Jenny is one of the Caribbean’s most active volcanoes. It sits eight kilometres off the northern coast of the island of Grenada, and was first discovered in 1939 when a 300-metre column of ash and dust was spotted rising from the ocean.
However, volcanic activity at KeJ is usually detected by accompanying seismic activity picked up on land-based seismometers. These recordings show that the volcano is active on a decadal timescale.
Lead author PhD student Robert Allen, from Imperial College, said: “There are surveys of the Kick-‘em-Jenny area going back 30 years, but our survey in April 2017 is unique in that it immediately followed an eruption. This gave us unprecedented data on what this volcanic activity actually looks like, rather than relying on interpreting seismic signals.”
The team, which included Liverpool's Professor Andreas Rietbrock, found that the volcano has frequent cycles of lava ‘dome’ growth followed by collapse through landslides. Similar cycles have been recently witnessed on the nearby volcanic island of Montserrat.
SRC Director Professor Richard Robertson said: “This study has confirmed very useful recent insights on the activity and evolution of Kick-‘em-Jenny volcano. For us, the agency with responsibility for monitoring this volcano, the results of this collaborative research project enable us to better quantify our existing model of this volcano and help in developing strategies for managing future eruptions.”
Any volcano on land which was as lively as KeJ would be constantly monitored by satellites and an array of local instruments looking for the slightest change in behaviour that could precede a major volcanic eruption.
Under the ocean this job is much more difficult, as the electromagnetic energy emitted by satellites cannot penetrate the sea surface and instruments are much more difficult to set up on the volcano itself. Scientists therefore know comparatively little about the growth and long-term behaviour of a fully submerged volcanic cone like KeJ.
The most famous submarine volcanoes are those that lead to the formation of new islands, such as the eruption of Surtsey in Iceland in the 1960s. However, rather than a growing cone, the surveys show significant mass loss from KeJ due to frequent landslides in recent decades.
Comparison with recent studies elsewhere has shown that similar, frequent, small volume landslides may be a fundamental mechanism in the long-term evolution of active submarine volcanoes.
The research paper `30 Years in the Life of an Active Submarine Volcano: A Time-Lapse Bathymetry Study of the Kick-‘em-Jenny Volcano, Lesser Antilles’ is published in Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems. DOI: 10.1002/2017GC007270
The research was by funded by NERC (the Natural Environment Research Council) as part of the VoiLA research project. This project, a multidisciplinary collaboration between UK universities and The University of the West Indies, aims to discover the role that volatile recycling plays in the growth of the Lesser Antilles island arc.